In India, vehicle insurance is not just a financial safeguard but a legal requirement under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988. Ensuring your vehicle has valid insurance protects you from penalties, covers third-party liabilities, and secures you against own-damage costs.
Checking your vehicle’s insurance status regularly helps avoid lapses, ensures timely renewals, and aids in accident-related claims.
This guide details both online and offline methods to verify your vehicle’s insurance status efficiently.
Online Methods to Check Vehicle Insurance Status
V A H A N | National Register e-Services
A centralized platform by the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways storing vehicle data. Steps:
- Visit official portal - https://vahan.parivahan.gov.in/nrservices/.
- Navigate to “Know Your Vehicle Details.”
- Log in or register using your mobile number.
- Enter the vehicle’s registration number and verify with the CAPTCHA.
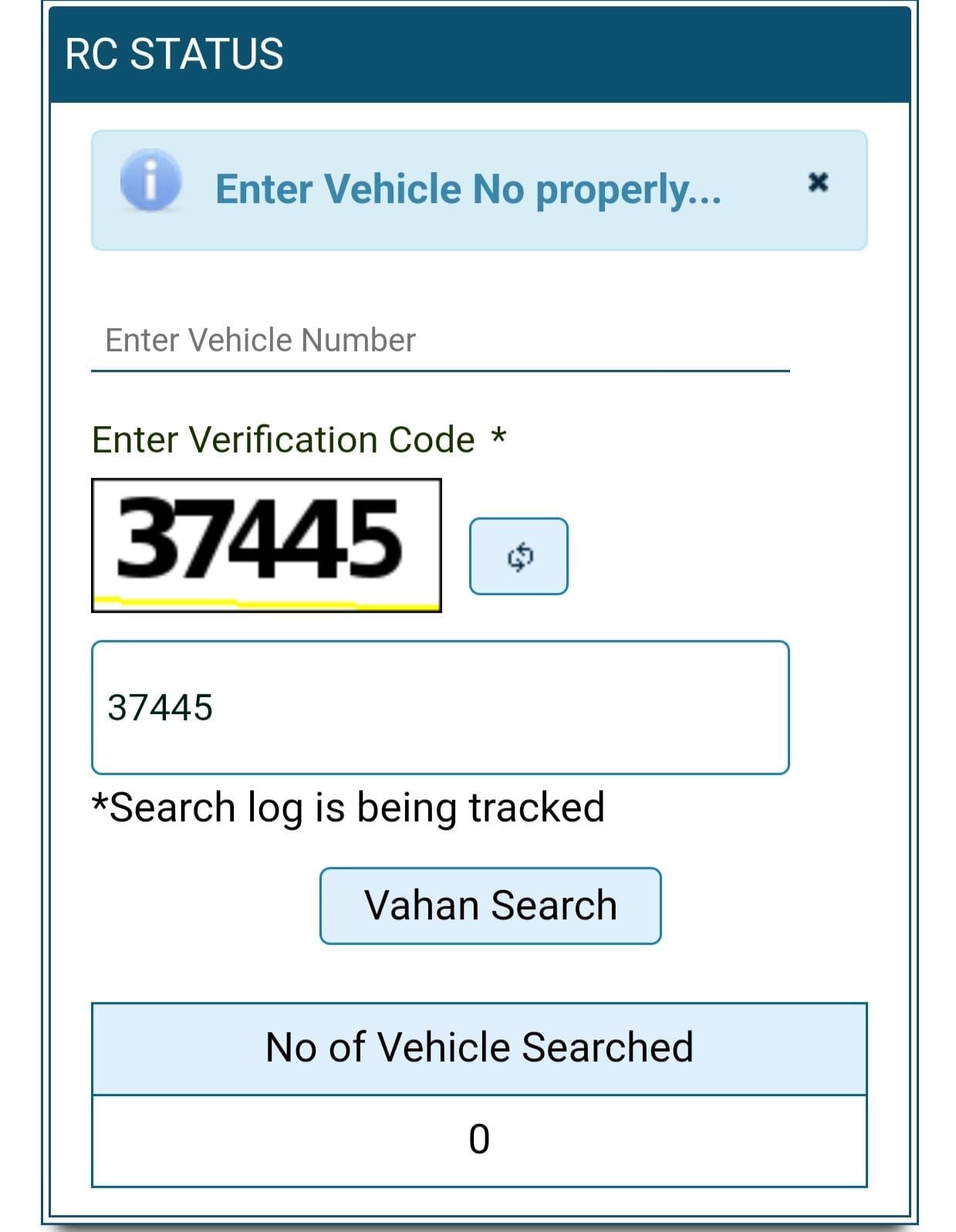
- View insurance details, including policy number, insurer, and expiry date.
2. Insurer’s Website or App
Most insurance providers offer online portals or mobile apps for policy management. Steps:
- Visit your insurer’s official website (e.g., HDFC Ergo, ICICI Lombard) or download their app.
- Log in with policyholder credentials or register using policy number.
- Enter vehicle registration or policy number.
- Check policy status, expiry date, and coverage details.
Popular Insurers:
- Bajaj Allianz: bajajallianz.com
- Reliance General: reliancegeneral.co.in
- Tata AIG: tataaig.com
Offline Methods to Check Vehicle Insurance Status
1. Visit the Regional Transport Office (RTO)
RTOs maintain vehicle records, including insurance details. Steps:
- Locate your nearest RTO office.
- Provide vehicle registration number and chassis/engine number.
- Request insurance status from the RTO official.
Documents Needed:
- Vehicle registration certificate (RC)
- Identity proof
- Insurance policy copy (if available)
2. Contact Insurance Provider
Directly reach out to your insurer for detailed information. Steps:
- Call the insurer’s customer care (e.g., toll-free numbers listed on their website).
- Provide policy number or vehicle registration details.
- Request policy status and validity.
3. Visit an Insurance Agent or Broker
If purchased through an agent, they can assist with status checks. Steps:
- Contact your agent with vehicle and policy details.
- Request them to verify insurance status via their portal.
Tips for Accurate Insurance Status Checks
- Keep Documents Ready: Vehicle registration number, chassis/engine number, and policy number are essential.
- Verify Data Entry: Double-check registration number format (e.g., DL05AB1234).
- Check Expiry Dates: Renew policies before expiry to avoid penalties.
- Cross-Verify: Use multiple methods (e.g., Parivahan and insurer’s portal) for accuracy.
- Beware of Fraud: Use only official websites and verified contact numbers.
Penalties for Driving Without Valid Insurance
In India, driving without valid insurance is illegal under the Motor Vehicles Act, 2019. Penalties include:
- First offence: ₹2,000 fine and/or up to 3 months imprisonment.
- Second offense: ₹4,000 fine and/or up to 3 months imprisonment.
Additional consequences:
- Vehicle seizure until valid insurance is shown.
- Personal liability for accident damages.
- Possible suspension of driving license or vehicle registration.
Applies to all vehicles (two-wheelers, four-wheelers, commercial).
Additional Tips
- Renew Early: Renew insurance 15–30 days before expiry to avoid lapses.
- Verify Third-Party Insurance: Mandatory for all vehicles; check via IIB or Parivahan.
- e-Vahan Bima: Use apps like mParivahan to store digital insurance copies.
- Fraud Prevention: Cross-check insurer details to avoid fake policies.
Difference Between First-Party and Third-Party Vehicle Insurance
Vehicle insurance in India ensures legal compliance and financial security. Third-party insurance, mandatory under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, covers damages to others, while optional first-party insurance protects the policyholder’s vehicle.
| Feature | First-Party Insurance | Third-Party Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Policyholder and their vehicle | Third parties (others’ property/people) |
| Scope | Own-damage (accidents, theft, fire, natural disasters) | Damages/injuries caused by your vehicle |
| Legal Requirement | Optional | Mandatory (Motor Vehicles Act, 1988) |
| Exclusions | Third-party damages | Policyholder’s vehicle damage |
| Example | Repairs for your car after a crash | Compensation for hitting another car |
Types of Vehicle Insurance Policies
- Comprehensive Insurance: Combines first-party and third-party coverage. Protects against own-damage (accidents, theft, natural calamities) and third-party liabilities. Includes add-ons like zero depreciation, roadside assistance.
- Standalone Own-Damage (OD) Insurance: Covers only the policyholder’s vehicle. Requires separate third-party policy to meet legal requirements.
- Pay-As-You-Drive Insurance: Premium based on kilometers driven. Ideal for low-usage vehicles.
- Bundled Policies: Combine third-party and own-damage for new vehicles (up to 3 years for two-wheelers, 1 year for four-wheelers).
Add-On Covers
Enhance comprehensive policies for extra protection:
- Zero Depreciation: Full claim without factoring in depreciation of parts.
- Roadside Assistance: Covers towing, fuel delivery, tire changes.
- No-Claim Bonus (NCB) Protection: Retains NCB discount despite claims.
- Engine Protection: Covers engine damage from water ingress or oil leaks.
- Personal Accident Cover: Compensation for death or disability of the policyholder.
Factors Affecting Premiums
- Vehicle Type: Higher for luxury or high-capacity vehicles.
- Age of Vehicle: Older vehicles may have higher premiums due to repair costs.
- Geographical Location: Urban areas with higher accident rates increase premiums.
- Driver’s Profile: Age, driving history, and claims affect rates.
- Add-Ons: Additional covers increase premium costs.
Claim Process
- Inform Insurer: Notify immediately after an incident.
- File FIR: For accidents, theft, or third-party claims.
- Submit Documents: Policy copy, RC, DL, FIR, repair bills.
- Survey: Insurer assesses damage for approval.
- Settlement: Cashless (network garage) or reimbursement.
Common Exclusions
- Wear and Tear: Normal ageing or mechanical failure not covered.
- Drunk-Driving: Claims denied if driver is intoxicated.
- Unlicensed Driver: No coverage if driver lacks a valid license.
- Non-Approved Modifications: After market changes may void claims.