Vehicle registration in India is a mandatory legal requirement under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, ensuring vehicles are identified, taxed, and insured for road use. Managed by Regional Transport Offices (RTOs), the process involves obtaining a Registration Certificate (RC) with a unique registration number.
This article outlines the types, procedures, documents, fees, and key considerations for vehicle registration.
Types of Vehicle Registration
| Type | Issuer | Validity | Format | Purpose/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temporary Registration | Dealer | 1 month (extendable for bodybuilding chassis) | TMMYYAAZZ (e.g., T1223AA1234) | Legal driving until permanent registration; "T" for temporary, MMYY for purchase month/year, AA for state code, ZZ for alphabetic sequence. |
| Permanent Registration | RTO (after application/verification) | 15 years (non-transport, renewable for 5 years); 20 years (commercial) | XX-YY-ZZ-1234 (e.g., MH-02-AB-1234) | Remains unchanged with ownership change; re-registration needed for interstate transfers. |
| Special Registration | RTO/Parivahan Portal | Varies (BH-Series: job duration; Vintage: rally use; Fancy: permanent) | BH: 22BH1234XX; VA: Vintage; Fancy: Custom | BH-Series for interstate job transfers; VA for 50+ year vehicles; Fancy via e-auction. |
Registration Process
The process can be completed via the dealer, an agent, or by the owner through the RTO or online Parivahan Sewa portal. Below is the self-registration procedure:
- Visit the Local RTO: Go to the RTO in whose jurisdiction you reside or operate your business within 7 days of vehicle purchase.
- Submit Application (Form 20):
- Fill and submit Form 20 (available at RTO or online via parivahan.gov.in).
- For hypothecated vehicles (on loan), include an additional Form 20 photocopy.
- Document Submission: Provide required documents (listed below) for verification by the RTO superintendent.
- Pay Fees and Taxes: Pay registration fees and road tax at the RTO counter or online. Road tax varies by state and vehicle type.
- Vehicle Inspection: Present the vehicle for inspection by the Inspector of Motor Vehicles (IMV) to verify chassis/engine numbers and roadworthiness.
- Data Entry and Approval:
- RTO enters vehicle details into the Vahan database.
- The Assistant Regional Transport Officer (ARTO) approves the registration.
- Issuance of RC: A RC is issued and mailed to the registered address, typically within a week.
Documents Required
- Form 20: Application for registration.
- Form 21: Sales certificate from the dealer.
- Form 22: Roadworthiness certificate from the manufacturer.
- Form 34: For hypothecated vehicles (if applicable).
- Identity Proof: Aadhaar, PAN, Voter ID, passport, or driving license.
- Address Proof: Aadhaar, Voter ID, ration card, utility bill, or rent agreement.
- Vehicle Insurance Certificate: Valid insurance policy.
- PUC Certificate: Pollution Under Control certificate.
- Invoice: Original retail and manufacturer invoice.
- Road Tax Receipt: If paid by the dealer.
- NOC: For vehicles bought in another state, include NOC from the original RTO and dealer.
- Additional for Re-Registration:
- Form 25: For RC renewal after 15 years.
- Form 27/28: For interstate transfers, with NOC from the original RTO, financier, and National Crime Record Bureau (NCRB).
- PAN card copy or Form 60/61 if PAN is unavailable.
- Fitness certificate for commercial vehicles.
Fees and Charges
- Registration Fees (as per Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989, subject to change):
- Two-wheelers: ₹300.
- Cars (non-transport): ₹600.
- Commercial vehicles: ₹1,000–₹1,500.
- Late renewal: ₹300/month (two-wheelers), ₹500/month (other non-transport vehicles).
- Road Tax: Varies by state (e.g., 4–10% of vehicle cost in most states).
- Fancy Number Fees: Determined via e-auction (e.g., ₹5,000–₹1 lakh for premium numbers like 0001).
- Smart Card Fee: ₹200–₹500.
- Hypothecation Charges: ₹500–₹1,500 for loan-financed vehicles.
Number Plate Specifications
- Issued under High Security Registration Plate (HSRP) rules.
- Font: Modern Latin letters and Arabic numerals.
- Color Coding:
- Private vehicles: Black letters on white background (e.g., DL-03-AB-1234).
- Commercial vehicles: Black letters on yellow background (e.g., MH-19-AG-5465).
- Rental vehicles: Yellow letters on black background.
- Diplomatic vehicles: White letters on light blue background.
- Temporary: Red letters on yellow background.
- Format: XX-YY-ZZ-1234 (XX: state code, e.g., DL for Delhi; YY: RTO code; ZZ: series; 1234: number).
Renewal and Re-Registration
- RC Renewal (after 15 years for non-transport vehicles):
- Submit Form 25, original RC, insurance, PUC, and tax receipt.
- Pay renewal fees and undergo a vehicle inspection.
- New RC valid for 5 years.
- Interstate Re-Registration:
- Required when moving to another state for over 12 months.
- Submit Form 27/28, original RC, NOCs (RTO, financier, NCRB), insurance, PUC, and tax receipts.
- Pay re-registration fees and new state’s road tax.
Vehicle Registration Status
To check Vehicle Registration Status:
- Visit the Transport Department portal: https://parivahan.gov.in/
- On the homepage, go to Online Services and click Vehicle Related Services.

- Select your State and RTO.
- You’ll be redirected to the Vehicle Citizen Portal.
- Click Status in the menu.
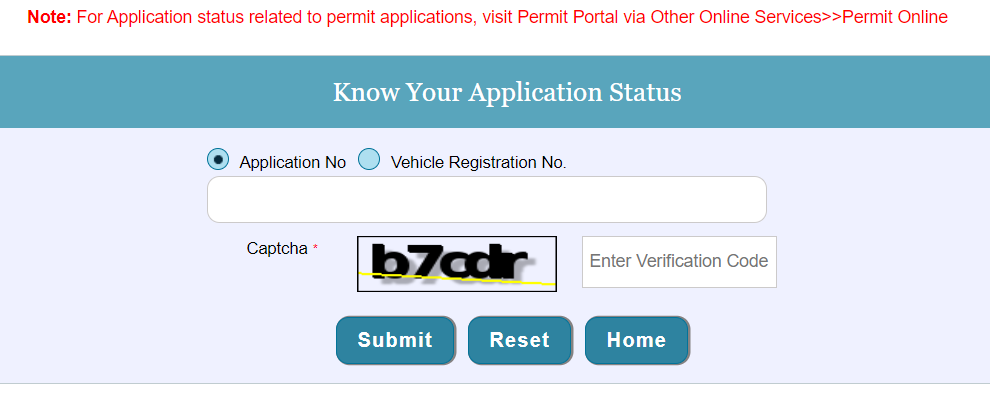
- Select Know Your Application Status.
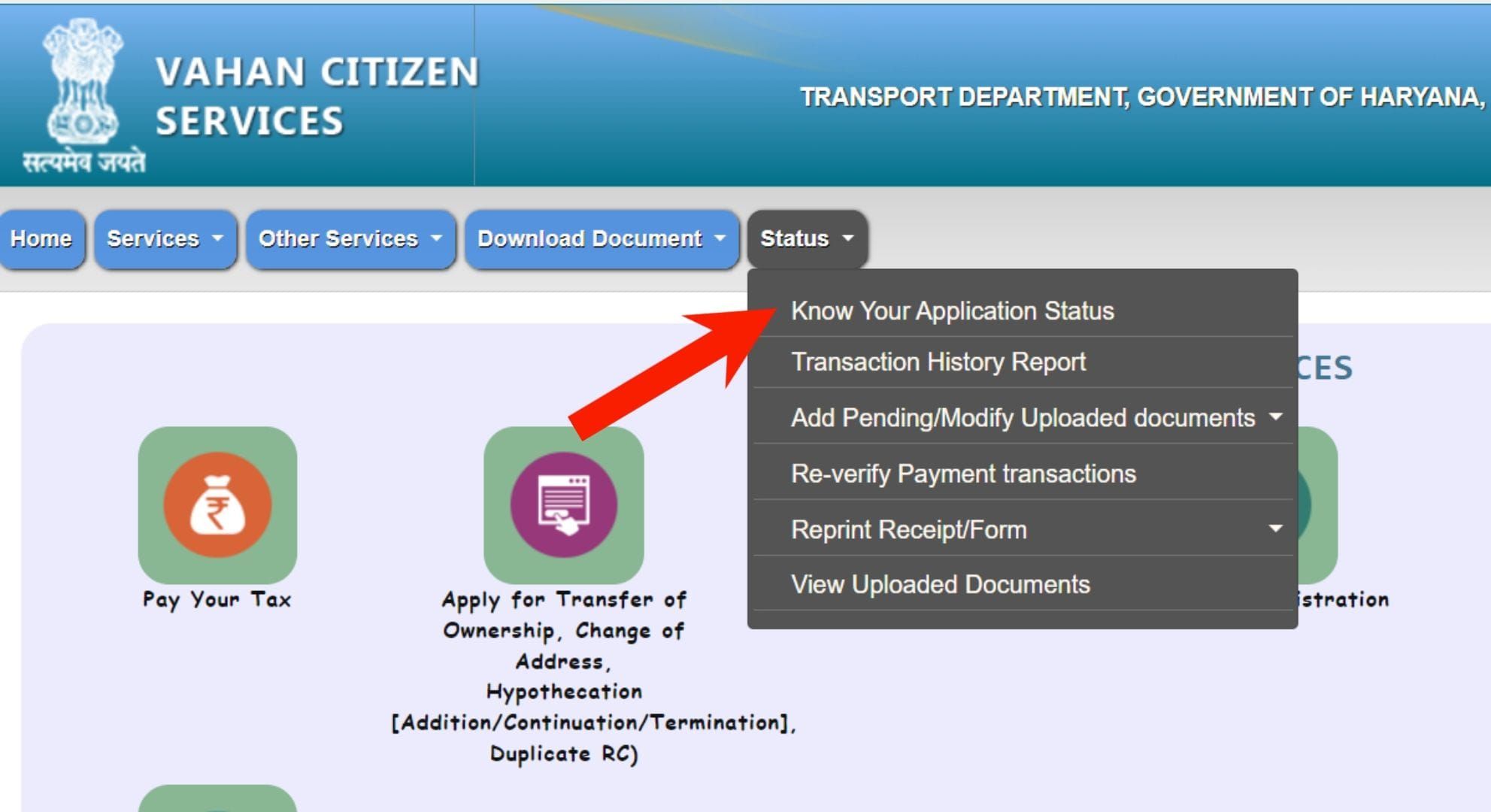
- Enter your Registration Number or Application Number and click Submit.
- Your vehicle registration status will appear on the screen.
💡
After issuing the permanent registration number, the RTO will provide a Registration Certificate (RC). This certificate is also available in digital format and can be stored securely in DigiLocker or the mParivahan app.