Selling a second-hand vehicle in India requires transferring ownership to the buyer to update legal records with the RTO. This process protects the seller from future liabilities (e.g., accidents, fines) and enables the buyer to register, insure, and use the vehicle legally.
The transfer can be initiated offline at the RTO or partially online through the Parivahan Sewa portal (parivahan.gov.in) in states like Delhi, Maharashtra, and Gujarat. Both methods involve specific documents, fees, and timelines, with variations by state and vehicle type.
Importance of Ownership Transfer
- Seller: Avoids liability for post-sale incidents, ensuring the vehicle is no longer linked to their name.
- Buyer: Gains legal ownership, enabling registration, insurance transfer, and future resale.
- RTO: Maintains accurate records for taxation, road safety, and enforcement.
Required Documents
The following documents are mandatory for both online and offline transfers:
- Registration Certificate (RC): Original RC book or smart card.
- Form 29: Notice of Transfer of Ownership (two copies, signed by seller and buyer).
- Form 30: Application for Transfer of Ownership (two copies, signed by both parties).
- Insurance Certificate: Valid policy in the seller’s name (buyer must transfer/renew post-sale).
- Pollution Under Control (PUC) Certificate: Valid, confirming emission compliance.
- No Objection Certificate (NOC):
- Bank NOC (Form 35): If the vehicle is under a loan, proving it’s cleared.
- RTO NOC: For interstate transfers, from the original RTO.
- Identity Proof: Aadhaar, PAN, passport, or voter ID for both parties.
- Address Proof: Aadhaar, utility bill, or rental agreement for both parties.
- PAN Card or Form 60: For tax compliance (mandatory for vehicles sold above ₹2 lakh).
- Passport-Size Photos: 2–3 recent photos of the buyer.
- Delivery Note (Optional): Records handover date, odometer reading, and vehicle condition.
- Tax Clearance: Proof of paid road tax and no pending fines (check via VAHAN portal).
Additional for Online Process:
- Scanned copies of all documents in PDF format.
- Aadhaar number for e-KYC verification (in states with online services).
- Digital signature (optional, for faster processing in some states).
Offline Process for Ownership Transfer
Step 1: Finalize the Sale
- Agree on the sale price, payment method, and handover date. A written sale agreement is advisable, detailing:
- Vehicle make, model, registration number, chassis/engine numbers.
- Sale price and payment terms.
- Handover date and vehicle condition.
- Verify the vehicle’s status on the VAHAN portal for loans, fines, or theft records.
- Clear any loan and obtain a bank NOC (Form 35) if applicable.
Step 2: Prepare Documents
- Collect all required documents listed above.
- Ensure Forms 29 and 30 are filled accurately and signed by both parties.
- Verify that RC, insurance, and PUC are valid and match the vehicle’s details.
Step 3: Visit the RTO
- Who Attends: Buyer, or both parties (state-dependent). The seller may submit Form 29 separately to notify the sale.
- Where: The RTO where the vehicle is registered.
- Submission:
- Submit Forms 29, 30, and supporting documents within 14 days (private vehicles) or 30 days (commercial vehicles).
- The RTO verifies documents, checks for fines/taxes, and may inspect the vehicle (chassis/engine numbers).
- Fees:
- Transfer fee: ₹50–₹500 (e.g., ₹150 for two-wheelers, ₹300 for cars).
- Smart card fee: ₹200–₹500 (if updating RC).
- Hypothecation removal: ₹100–₹500 (if applicable).
- Road tax (interstate): 2%–12% of depreciated value.
- Service charges: ₹50–₹200.
Step 4: Receive Updated RC
- The RTO processes the transfer within 2–4 weeks.
- The buyer receives a new RC book or smart card in their name.
- For interstate transfers, a new registration number may be issued.
Online Process for Ownership Transfer
The Parivahan Sewa portal offers partial online processing in states like Delhi, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, and Uttar Pradesh. Physical RTO visits may still be required for verification.
Step 1: Finalize the Sale
- Same as offline: Agree on terms, verify vehicle status, and clear loans if applicable.
Step 2: Access Parivahan Portal
- Visit parivahan.gov.in.
- Navigate to “Vehicle Related Services” and select the state/RTO.
- Enter the vehicle’s registration number to retrieve details.
- On the new page, you'll see the "Apply For Ownership Transfer" option; click it.
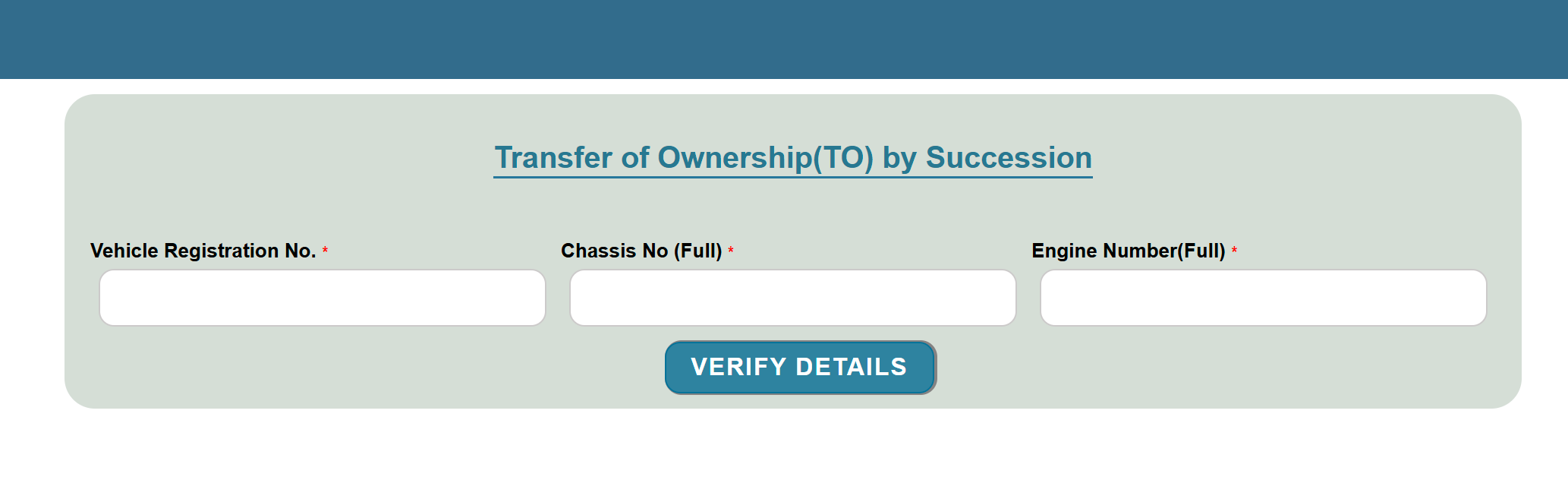
- A new page will open where you enter your vehicle registration number and chassis number, then click "Verify Details."
- Next, click "Transfer of Ownership" in the Application Section.
Now, under "Transfer of Ownership Details," enter the following:- New owner's details
- Current address
- Permanent address
- Insurance details
Then, on the next page, pay the fee.
Step 3: Fill and Upload Forms
- Download Forms 29 and 30 from the portal.
- Fill both forms (two copies each), sign digitally (if available) or physically, and scan as PDFs.
- Upload scanned documents:
- RC, insurance, PUC, identity/address proofs, PAN/Form 60.
- Bank NOC (if applicable) and RTO NOC (for interstate transfers).
- Buyer’s photos.
- Complete e-KYC using Aadhaar for both parties (mandatory in some states).
Step 4: Pay Fees Online
- Use the portal’s fee calculator to determine costs:
- Transfer fee: ₹50–₹500.
- Smart card fee: ₹200–₹500.
- Hypothecation removal: ₹100–₹500.
- Road tax (interstate): Varies by state/vehicle.
- Pay via net banking, UPI, or card. Save the payment receipt.
Step 5: RTO Verification
- After online submission, the RTO reviews documents (1–2 weeks).
- The buyer (or both parties) may need to visit the RTO for:
- Physical document submission.
- Vehicle inspection (chassis/engine numbers).
- Some states (e.g., Delhi) allow fully online processing for same-state transfers, with RC mailed to the buyer.
Step 6: Receive Updated RC
- The RTO updates the RC within 2–4 weeks.
- The buyer receives the new RC (smart card/book) by post or at the RTO.
- Interstate transfers may require re-registration and a new number.
Special Cases
| Situation | Transfer Process Details |
|---|---|
| General Sale Transfer Process | Vehicle registered in new owner's name upon sale. Submit Forms 29 and 30, insurance certificate, address proof, etc. Registration certificate issued to new owner after fee payment. |
| Vehicle Transfer on Owner's Death | Ownership transferred to deceased owner's legal heir. Heir must notify RTO within 30 days, submit death certificate, succession certificate, etc. |
| Transfer of Vehicle Bought at Auction | Ownership transferred to new buyer. Auction documents, receipt, and other required documents submitted to RTO. |
| Interstate Transfers | Obtain RTO NOC (Form 28) from original RTO (1–2 weeks). Submit NOC, Forms 27/29/30, and documents to new state’s RTO. Pay road tax (2%–12%) and re-registration fees. Online: Apply for NOC via Parivahan, upload documents to new state’s RTO portal, physical visit often required. |
| Financed Vehicles | Seller clears loan, obtains bank NOC (Form 35). Submit NOC to RTO to remove hypothecation (₹100–₹500). Buyer verifies loan status on VAHAN. Online: Limited support. |
| Sale to a Dealer | Seller submits Form 29 to notify sale; dealer handles buyer-side transfer. Online: Limited support, physical forms often required. |